Embark on a captivating journey with the Earthquakes and Volcanoes Webquest Answer Key, your authoritative guide to understanding the enigmatic forces that shape our planet. This comprehensive resource unveils the intricacies of earthquakes and volcanoes, empowering you with knowledge to navigate their potential impacts.
Delve into the depths of seismic activity and volcanic eruptions, exploring their causes, effects, and the methodologies employed to measure and predict these natural phenomena. Discover the strategies implemented to mitigate their devastating consequences, ensuring preparedness and resilience in the face of these formidable forces.
1. Introduction
Earthquakes and volcanoes are two of the most powerful and destructive forces on Earth. They can cause widespread damage and loss of life, and they can have a profound impact on the environment.
In this webquest, we will explore the causes, effects, and mitigation of earthquakes and volcanoes. We will also learn how scientists measure and predict these natural disasters.
1.1 Definition of Earthquakes and Volcanoes
An earthquake is a sudden, rapid shaking of the Earth’s crust. Earthquakes are caused by the release of energy below the Earth’s surface. Volcanoes are mountains that form when magma, or molten rock, rises from the Earth’s mantle and erupts onto the surface.
1.2 Types of Earthquakes and Volcanoes
There are many different types of earthquakes and volcanoes. Earthquakes can be classified by their magnitude, which is a measure of the energy released by the earthquake. Volcanoes can be classified by their shape, their eruptive style, and the type of magma they produce.
1.3 Causes of Earthquakes and Volcanoes
Earthquakes are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Tectonic plates are large pieces of the Earth’s crust that are constantly moving. When two tectonic plates collide, one plate may be forced to move beneath the other. This process, called subduction, can cause earthquakes.
Volcanoes are caused by the movement of magma. Magma is molten rock that is found beneath the Earth’s surface. When magma rises to the surface, it can erupt through a volcano.
2. The Effects of Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Earthquakes And Volcanoes Webquest Answer Key
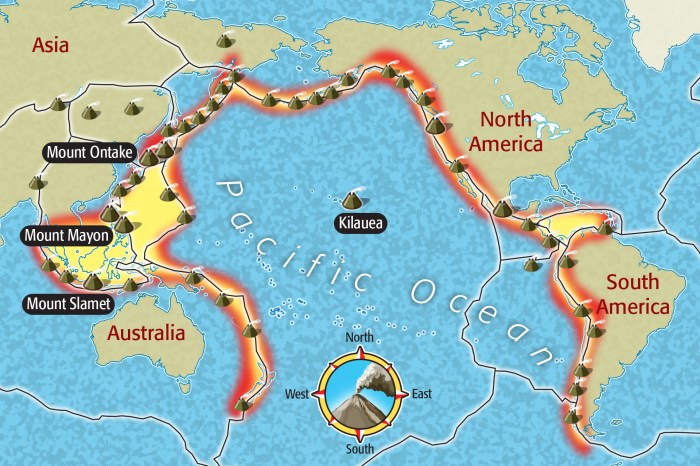
Earthquakes and volcanoes can have a devastating impact on the environment. Earthquakes can cause landslides, tsunamis, and fires. Volcanoes can erupt ash, lava, and gas, which can pollute the air and water.
2.1 Effects of Earthquakes on the Environment
- Landslides: Earthquakes can trigger landslides, which are the rapid movement of large amounts of earth and rock down a slope.
- Tsunamis: Earthquakes can also trigger tsunamis, which are large waves that can travel across the ocean and cause widespread damage.
- Fires: Earthquakes can also cause fires, which can spread quickly and destroy homes and businesses.
2.2 Effects of Volcanoes on the Environment, Earthquakes and volcanoes webquest answer key
- Ash: Volcanoes can erupt ash, which is a fine powder that can travel long distances and block out the sun.
- Lava: Volcanoes can also erupt lava, which is molten rock that can flow down the sides of a volcano and destroy everything in its path.
- Gas: Volcanoes can also erupt gas, which can pollute the air and water.
2.3 Effects of Earthquakes and Volcanoes on Human Populations
- Death and injury: Earthquakes and volcanoes can cause widespread death and injury. In the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami, more than 15,000 people were killed.
- Homelessness: Earthquakes and volcanoes can also cause widespread homelessness. In the 2010 Haiti earthquake, more than 1 million people were left homeless.
- Economic damage: Earthquakes and volcanoes can also cause significant economic damage. In the 1994 Northridge earthquake, the damage was estimated to be more than $20 billion.
3. Measuring and Predicting Earthquakes and Volcanoes
Scientists use a variety of methods to measure and predict earthquakes and volcanoes. These methods include:
3.1 Measuring Earthquakes
- Seismographs: Seismographs are instruments that measure the ground motion caused by earthquakes.
- Accelerographs: Accelerographs are instruments that measure the acceleration of the ground during an earthquake.
3.2 Predicting Earthquakes
Scientists are still working on developing reliable methods for predicting earthquakes. However, there are a number of factors that can be used to assess the risk of an earthquake in a particular area. These factors include:
- Historical earthquake data: Scientists can use historical earthquake data to identify areas that are at high risk for future earthquakes.
- Geologic data: Scientists can also use geologic data to identify areas that are at high risk for earthquakes. For example, areas with active faults are more likely to experience earthquakes.
- Geodetic data: Scientists can also use geodetic data to measure the movement of the Earth’s crust. This data can be used to identify areas that are at high risk for earthquakes.
3.3 Predicting Volcanoes
Scientists are also working on developing reliable methods for predicting volcanic eruptions. However, there are a number of factors that can be used to assess the risk of a volcanic eruption in a particular area. These factors include:
- Historical eruption data: Scientists can use historical eruption data to identify volcanoes that are at high risk for future eruptions.
- Geologic data: Scientists can also use geologic data to identify volcanoes that are at high risk for eruptions. For example, volcanoes with a history of frequent eruptions are more likely to erupt again.
- Geochemical data: Scientists can also use geochemical data to measure the composition of volcanic gases. This data can be used to identify volcanoes that are at high risk for eruptions.
4. Mitigating the Effects of Earthquakes and Volcanoes
There are a number of things that can be done to mitigate the effects of earthquakes and volcanoes. These measures include:
4.1 Mitigating the Effects of Earthquakes
- Building codes: Building codes can be used to ensure that buildings are designed to withstand earthquakes.
- Land use planning: Land use planning can be used to identify areas that are at high risk for earthquakes and to restrict development in these areas.
- Public education: Public education can help people to understand the risks of earthquakes and to take steps to protect themselves.
4.2 Mitigating the Effects of Volcanoes
- Volcano monitoring: Volcano monitoring can be used to track the activity of volcanoes and to provide early warning of eruptions.
- Evacuation plans: Evacuation plans can be developed to help people to evacuate safely in the event of a volcanic eruption.
- Public education: Public education can help people to understand the risks of volcanoes and to take steps to protect themselves.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the primary causes of earthquakes?
Earthquakes are primarily triggered by the sudden release of energy within the Earth’s crust, often caused by the movement of tectonic plates along fault lines.
How can we predict the occurrence of volcanic eruptions?
Predicting volcanic eruptions is a complex task, but scientists employ various methods, such as monitoring seismic activity, analyzing gas emissions, and observing ground deformation.
What measures can be taken to mitigate the effects of earthquakes?
Earthquake mitigation strategies include constructing earthquake-resistant buildings, implementing early warning systems, and educating communities about preparedness measures.