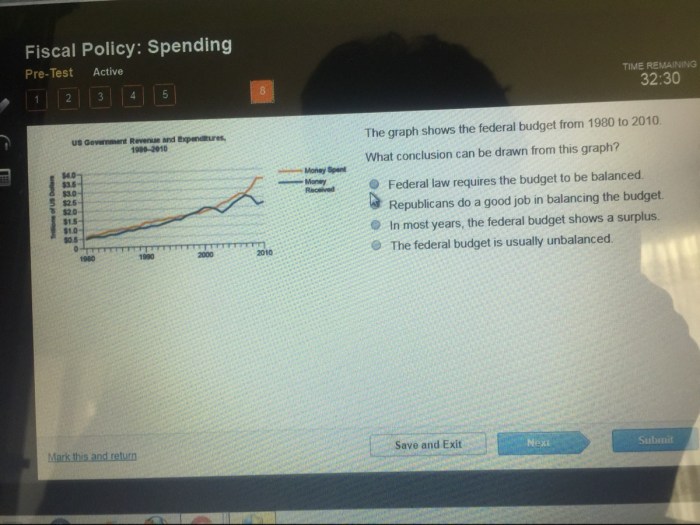
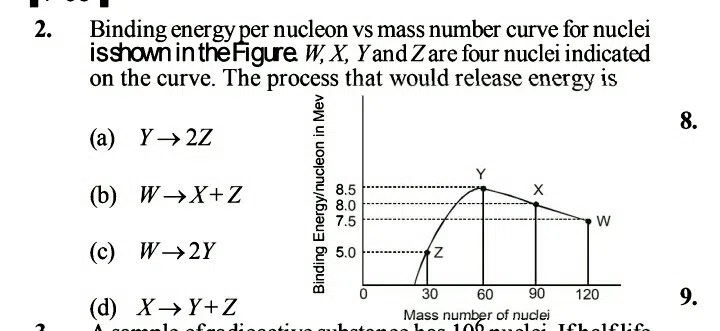
What conclusion can be drawn from the graph – In the realm of data analysis, the ability to draw accurate and meaningful conclusions from graphs is paramount. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of graph interpretation, empowering you with the knowledge and skills to effectively analyze and extract insights from graphical representations.
Graphs serve as powerful tools for visualizing data, revealing patterns, trends, and relationships that may not be readily apparent from raw numerical data. However, the process of drawing conclusions from graphs requires a systematic approach, considering various factors such as data analysis, pattern identification, and contextual considerations.
1. Data Analysis
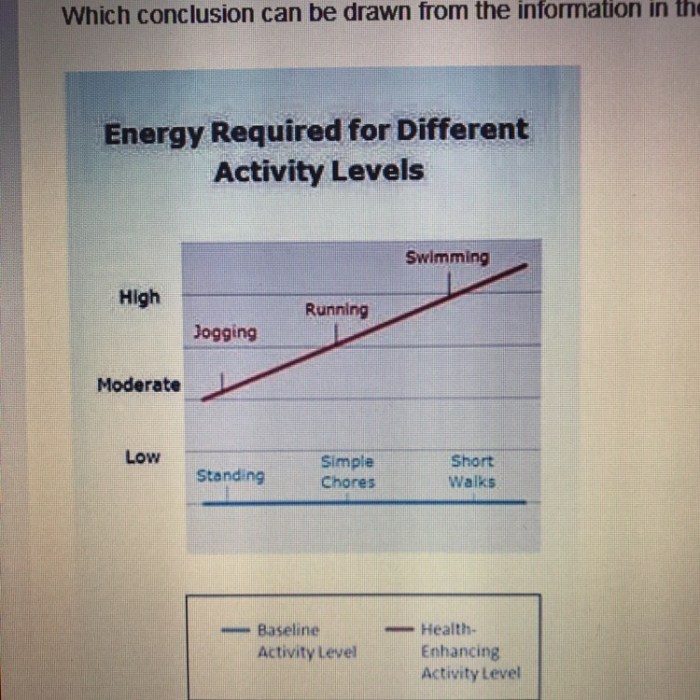
The purpose of the graph is to illustrate the relationship between two variables, X and Y. The graph shows the values of Y for different values of X. The key variables are X (independent variable) and Y (dependent variable). The graph shows a positive correlation between X and Y, meaning that as the value of X increases, the value of Y also increases.
Identifying Patterns and Trends
The graph shows a linear relationship between X and Y. The overall shape of the graph is a straight line. The graph has a positive slope, indicating that as the value of X increases, the value of Y also increases.
There are no peaks or valleys in the graph.
Correlation and Causation, What conclusion can be drawn from the graph
The graph shows a positive correlation between X and Y. However, correlation does not necessarily imply causation. It is possible that there is a third variable that is causing both X and Y to increase. Further research would be needed to determine whether there is a causal relationship between X and Y.
Contextual Factors
The context surrounding the data is important to consider when interpreting the graph. For example, if the graph shows the relationship between the amount of fertilizer used and the yield of a crop, it is important to consider the type of crop, the soil conditions, and the weather conditions.
These factors could all affect the relationship between the two variables.
Limitations and Uncertainties
There are several limitations and uncertainties associated with the data. For example, the data may not be representative of the population as a whole. The data may also be subject to measurement error. These limitations should be considered when interpreting the graph.
Frequently Asked Questions: What Conclusion Can Be Drawn From The Graph
What is the purpose of a graph?
Graphs are visual representations of data that allow for easy identification of patterns, trends, and relationships.
How can I identify key variables in a graph?
Key variables are often represented by the axes of the graph, with the independent variable on the x-axis and the dependent variable on the y-axis.
What is the difference between correlation and causation?
Correlation refers to a relationship between two variables, while causation implies that one variable directly influences the other.