Geneticists investigated the mode of inheritance, embarking on a quest to decipher the enigmatic patterns that govern the transmission of traits from one generation to the next. Their meticulous research has illuminated our understanding of genetic inheritance, paving the way for advancements in medicine, agriculture, and evolutionary biology.
Through rigorous methods and groundbreaking discoveries, geneticists have uncovered the secrets of genetic inheritance, shedding light on the mechanisms that determine our physical characteristics, predispositions to diseases, and even our behaviors. Their work has not only expanded our knowledge of human biology but also laid the foundation for personalized medicine and genetic counseling, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Overview of Geneticists’ Investigations
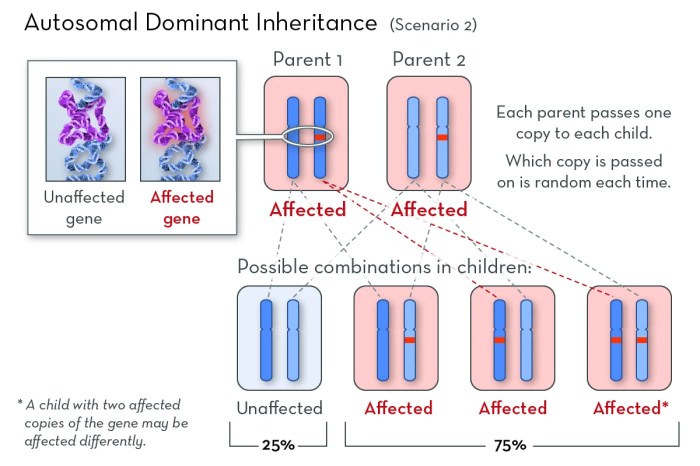
Geneticists play a pivotal role in studying inheritance patterns, the transmission of traits from one generation to the next. They investigate the genetic basis of traits, analyze inheritance modes, and identify genetic factors contributing to various characteristics and disorders.
Genetic traits can be physical, biochemical, or behavioral. Examples include eye color, blood type, susceptibility to certain diseases, and personality traits. Geneticists study the inheritance of these traits to understand the underlying genetic mechanisms and their impact on individuals and populations.
Methods of Inheritance Analysis: Geneticists Investigated The Mode Of Inheritance
Geneticists employ various methods to investigate inheritance patterns:
- Pedigree Analysis:Pedigree charts depict family relationships and the occurrence of traits over multiple generations, allowing researchers to identify patterns of inheritance and estimate the risk of inheriting certain traits.
- Twin Studies:Comparing identical (monozygotic) and fraternal (dizygotic) twins helps determine the relative contributions of genetics and environment to trait variation. Identical twins share 100% of their genes, while fraternal twins share only 50%, enabling researchers to isolate genetic influences.
- Genetic Mapping:This technique identifies the specific location of genes on chromosomes. By analyzing genetic markers linked to traits of interest, geneticists can map the inheritance patterns and identify genes responsible for specific traits.
Each method has its strengths and limitations. Pedigree analysis is relatively simple and cost-effective but limited by the availability of accurate family history. Twin studies provide valuable insights into the genetic basis of traits but can be confounded by environmental factors.
Genetic mapping is highly precise but can be technically challenging and expensive.
Patterns of Inheritance
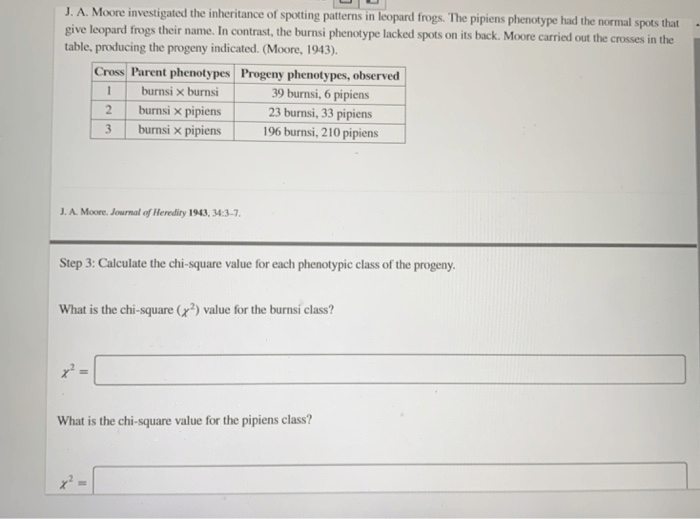
Geneticists have identified different patterns of inheritance:
Mendelian Inheritance, Geneticists investigated the mode of inheritance
Mendel’s laws of inheritance describe the transmission of single-gene traits. Each parent contributes one allele for each gene, and the offspring inherit a combination of these alleles. Dominant alleles are expressed even if paired with a recessive allele, while recessive alleles are only expressed when paired with another recessive allele.
Polygenic Inheritance
Polygenic traits are influenced by multiple genes, each with a small effect. The combined effect of these genes determines the phenotype. Polygenic inheritance is common for complex traits like height, weight, and skin color.
Mitochondrial Inheritance
Mitochondrial DNA is inherited exclusively from the mother. This type of inheritance is important for studying maternal lineages and understanding mitochondrial disorders.
Genetic Disorders and Inheritance

Geneticists study the inheritance of genetic disorders to understand their causes, patterns of transmission, and potential treatments. Genetic disorders can be caused by mutations in single genes (monogenic disorders) or by complex interactions between multiple genes and environmental factors (multifactorial disorders).
Examples of monogenic disorders include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington’s disease. Multifactorial disorders include heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
Genetic counseling plays a crucial role in understanding and managing inherited disorders. Genetic counselors provide information about the inheritance patterns of disorders, the risks of passing them on to offspring, and available options for prevention and treatment.
Ethical Considerations in Genetic Research
Genetic research on inheritance raises ethical implications:
- Informed Consent:Individuals participating in genetic research must provide informed consent, fully understanding the potential risks and benefits.
- Privacy:Genetic information is highly sensitive and should be protected from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Genetic Discrimination:Genetic information could be used to discriminate against individuals based on their genetic makeup, leading to unfair treatment in employment, insurance, and healthcare.
Ethical guidelines and regulations are essential to ensure that genetic research is conducted responsibly, protecting the rights and privacy of individuals while advancing scientific knowledge.
Top FAQs
What is the role of geneticists in studying inheritance patterns?
Geneticists play a crucial role in studying inheritance patterns by analyzing genetic data, conducting experiments, and developing models to understand how traits are passed down from parents to offspring.
What are the different methods used by geneticists to investigate inheritance?
Geneticists employ various methods to investigate inheritance, including pedigree analysis, twin studies, genetic mapping, and genome sequencing, each with its own strengths and limitations.
What are the different patterns of inheritance?
Inheritance patterns can be classified into Mendelian inheritance, polygenic inheritance, mitochondrial inheritance, and more complex patterns involving multiple genes and environmental factors.
How do geneticists study the inheritance of genetic disorders?
Geneticists study the inheritance of genetic disorders by analyzing family histories, conducting genetic tests, and identifying the specific genetic mutations responsible for the disorder.
What are the ethical considerations in genetic research on inheritance?
Genetic research on inheritance raises ethical concerns related to informed consent, privacy, genetic discrimination, and the potential misuse of genetic information.