CPT code ganglion cyst excision takes center stage in this informative article, providing readers with an in-depth exploration of this common medical procedure. We delve into the intricacies of ganglion cyst formation, diagnosis, and treatment options, offering valuable insights and practical guidance for both patients and healthcare professionals.
As we navigate the complexities of ganglion cyst excision, we uncover the latest advancements in surgical techniques, postoperative care, and recovery protocols. With a focus on accuracy and clarity, this article empowers individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Introduction

This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of ganglion cyst excision, a common surgical procedure to remove these benign fluid-filled swellings that often develop around joints or tendons.
Ganglion cysts are relatively prevalent, affecting approximately 1 in 20 individuals. Excision is a common treatment option, with over 100,000 procedures performed annually in the United States alone.
Anatomy and Pathophysiology
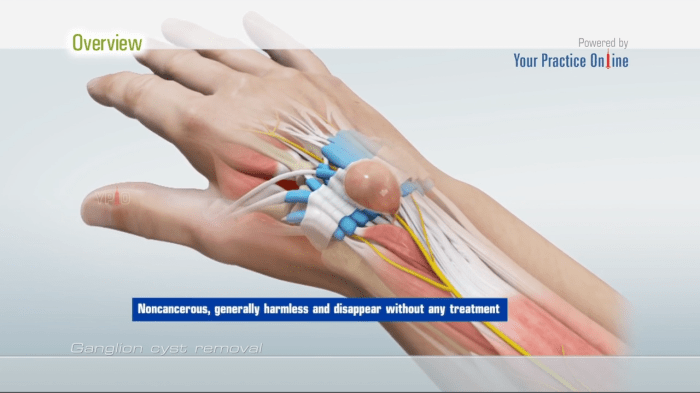
The wrist and hand are intricate structures composed of bones, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Ganglion cysts are fluid-filled sacs that commonly develop on the wrist or hand, often near joints or tendon sheaths.
Location and Structure of Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts can occur in various locations within the wrist and hand. The most common site is the dorsal wrist, where they arise from the scapholunate joint or the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC). Other potential locations include the volar wrist, the base of the thumb, and the fingers.
Ganglion cysts have a characteristic appearance, typically presenting as firm, round or oval swellings. They can vary in size, ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter.
Pathophysiology of Ganglion Cyst Formation
The exact cause of ganglion cyst formation is not fully understood. However, several theories and risk factors have been proposed:
- Mucoid Degeneration Theory:This theory suggests that ganglion cysts arise from the degeneration of connective tissue, leading to the formation of a fluid-filled cavity.
- Herniation Theory:According to this theory, ganglion cysts develop due to the herniation of synovial fluid from a joint or tendon sheath through a weakened area in the surrounding capsule or ligament.
Risk factors associated with ganglion cyst formation include:
- Repetitive wrist or hand movements
- Trauma or injury to the wrist or hand
- Certain medical conditions, such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
Understanding the anatomy and pathophysiology of ganglion cysts is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
Ganglion cysts commonly present with a palpable lump or swelling in the affected area. The lump is typically firm and non-tender, and it may be associated with pain, numbness, or tingling in the surrounding area. The symptoms can vary depending on the location of the cyst.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, the doctor will palpate the affected area to assess the size, consistency, and tenderness of the cyst. The doctor may also perform a range of motion tests to determine if the cyst is causing any functional limitations.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies, such as X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans, can be used to confirm the diagnosis of a ganglion cyst. These studies can help to differentiate ganglion cysts from other conditions, such as tumors or other types of cysts.
Aspiration
In some cases, the doctor may aspirate the cyst to remove the fluid and confirm the diagnosis. The fluid is typically clear and viscous, and it may contain cholesterol crystals.
Treatment Options
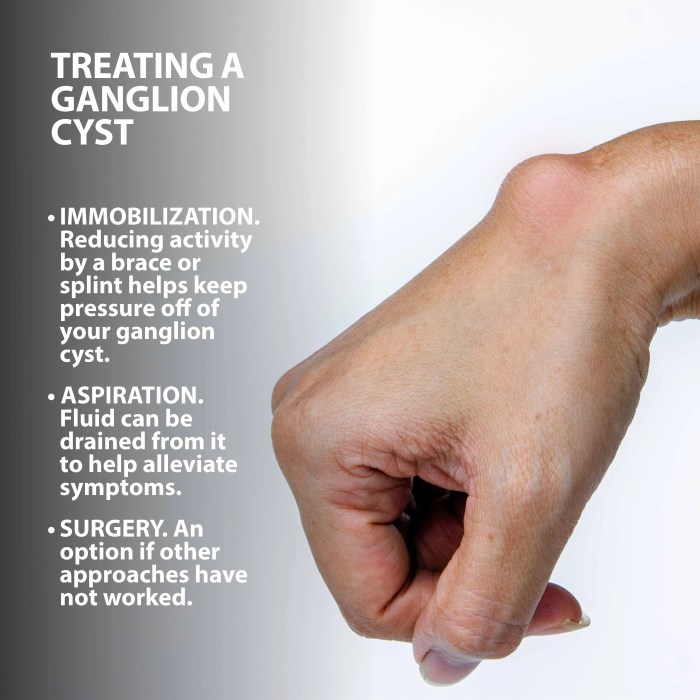
Ganglion cysts can be managed conservatively or treated with aspiration or surgical excision. The choice of treatment depends on the size, location, and symptoms of the cyst.
Conservative management involves observing the cyst and avoiding activities that aggravate it. Aspiration involves using a needle and syringe to remove the fluid from the cyst. Surgical excision involves removing the entire cyst.
Conservative Management
- Observation: This is the simplest and least invasive treatment option. It is suitable for small, asymptomatic cysts.
- Activity modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate the cyst can help to reduce pain and discomfort.
- Splinting: Splinting the affected joint can help to immobilize the cyst and reduce pain.
Aspiration
- Indications: Aspiration is indicated for cysts that are causing pain or discomfort. It is also used to confirm the diagnosis of a ganglion cyst.
- Contraindications: Aspiration is not recommended for cysts that are infected or located near major nerves or blood vessels.
- Complications: Aspiration can cause bleeding, infection, or damage to the surrounding tissues.
Surgical Excision
- Indications: Surgical excision is indicated for cysts that are large, painful, or causing nerve damage. It is also used to treat cysts that have recurred after aspiration.
- Contraindications: Surgical excision is not recommended for cysts that are located near major nerves or blood vessels.
- Complications: Surgical excision can cause bleeding, infection, or damage to the surrounding tissues.
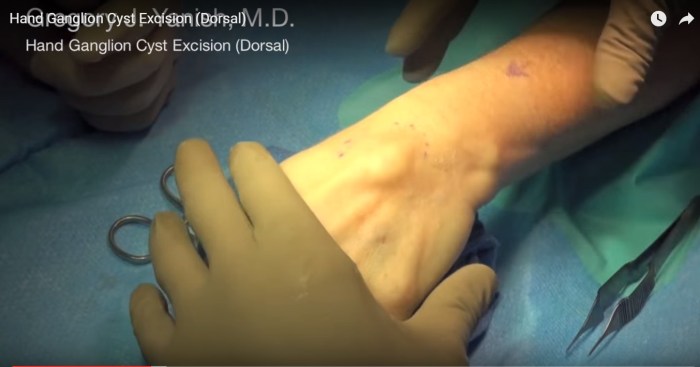
Surgical Excision Technique
Ganglion cyst excision is a surgical procedure to remove a ganglion cyst. It is typically performed on an outpatient basis, meaning the patient can go home the same day.
Preoperative Preparation
Before the surgery, the patient will be asked to:
- Fast for 8 hours before the surgery.
- Avoid taking any blood thinners or anti-inflammatory medications for a week before the surgery.
- Shower with antibacterial soap the night before and the morning of the surgery.
Anesthesia
The surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia, which means that only the area around the cyst will be numbed. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used if the cyst is large or located in a difficult-to-reach area.
Incision
The surgeon will make a small incision over the cyst. The size of the incision will depend on the size and location of the cyst.
Cyst Removal
The surgeon will carefully dissect the cyst from the surrounding tissue. The cyst will then be removed in one piece.
Wound Closure
The surgeon will close the incision with stitches or surgical glue. The wound will be covered with a bandage.
If you’re looking for the answer to the crossword clue “from south asia”, you’ll find it here . But if you’re interested in learning more about CPT code ganglion cyst excision, read on. Ganglion cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on the wrist or ankle.
They are usually benign, but they can cause pain and discomfort. CPT code ganglion cyst excision is the procedure used to remove these cysts.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
After ganglion cyst excision, patients typically experience minimal discomfort and can resume normal activities within a few days. The postoperative care instructions are as follows:
Wound Care:Keep the wound clean and dry. Change the dressing as directed by your doctor.
Activity:Avoid strenuous activity that could put pressure on the incision. You may gradually increase your activity level as tolerated.
Pain Management:Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help relieve discomfort.
Follow-up:Schedule a follow-up appointment with your doctor to check the wound and ensure proper healing.
Expected Recovery Time
Most patients can expect to recover fully within 2-4 weeks. However, the recovery time can vary depending on the size and location of the cyst.
Potential Complications
Complications after ganglion cyst excision are rare, but may include:
- Infection
- Recurrence of the cyst
- Nerve damage
- Scarring
Rehabilitation Protocols
Your doctor may recommend physical therapy or occupational therapy to help regain range of motion and strength in the affected area.
Outcomes and Prognosis: Cpt Code Ganglion Cyst Excision

The success rate of ganglion cyst excision is generally high, with most patients experiencing significant pain relief and improvement in hand function.
Recurrence rates vary depending on the size, location, and age of the patient. Smaller cysts that are located in easily accessible areas, such as the wrist, tend to have lower recurrence rates than larger cysts that are located in more complex areas, such as the palm or fingers.
Younger patients also tend to have higher recurrence rates than older patients.
Factors Affecting Prognosis
- Cyst Size:Larger cysts are more likely to recur after excision.
- Cyst Location:Cysts that are located in more complex areas, such as the palm or fingers, are more likely to recur after excision.
- Patient Age:Younger patients are more likely to have recurrence of ganglion cysts after excision.
Case Studies or Illustrative Examples
Ganglion cyst excision procedures vary in complexity and approach based on the cyst’s location and size. Here are some illustrative examples:
A 28-year-old female presented with a painless, firm, and mobile lump on her wrist. Preoperative ultrasound confirmed a ganglion cyst measuring 2 cm in diameter. Surgical excision was performed under local anesthesia, and the cyst was successfully removed. The patient experienced minimal discomfort and resumed normal activities within a week.
Postoperative Outcomes, Cpt code ganglion cyst excision
- The patient reported complete resolution of pain and lump.
- There were no complications or recurrence at the 6-month follow-up.
Top FAQs
What is a ganglion cyst?
A ganglion cyst is a fluid-filled sac that commonly develops on the wrist or hand. It is typically benign and can vary in size from a small pea to a large grape.
What are the symptoms of a ganglion cyst?
Ganglion cysts often cause pain, tenderness, and swelling in the affected area. They may also interfere with movement and grip strength.
How is a ganglion cyst diagnosed?
Ganglion cysts are typically diagnosed through a physical examination and medical history. Imaging studies, such as X-rays or ultrasounds, may be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
What are the treatment options for a ganglion cyst?
Treatment options for ganglion cysts include conservative management, aspiration, and surgical excision. Conservative management involves rest, splinting, and activity modification. Aspiration involves draining the fluid from the cyst using a needle and syringe. Surgical excision involves removing the cyst entirely.
What is the recovery time after ganglion cyst excision?
The recovery time after ganglion cyst excision typically ranges from a few days to a few weeks. Most patients can resume normal activities within a few days, but it may take several weeks for the incision to fully heal.